Amenorrhoea
Amenorrhoea means the absence of a menstrual circle in females. these are two types of primary or secondary.
Primary amenorrhoea means failure of a period to start by the age of 16, in the presence of otherwise normal growth and development of secondary sexual characteristics (breast development, pubic hair).
Secondary amenorrhoea means cessation of periods for six months or more after normal puberty and menstruation have occurred.
What is menstruation?
Menstruation is the cyclical loss of the endometrium layer of the uterus, which occurs as a result of a complex interaction between hormones in the brain and the ovaries.
The normal menstrual cycle is about 28 days and starts on the first day of menses.
the whole, menstrual periods are divided 3 phase these are..
1 Follicular phase.
2 ovulatory phase.
3 Luteal phase.
1 Follicular phase.
The follicular phase starts on the first day of menses and ends with ovulation. During the first 14 days of this cycle known as the follicular phase.In this phase
the hypothalamus releases a hormone called gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which stimulates the release of two hormones (follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)) from the pituitary gland.
2 ovulatory.
In the middle of this cycle, the ovary is stimulated to release an egg in a process called ovulation.
Duration of the ovulatory phase is the end of the follicular phase and the beginning of the luteal phase.
3 luteal phase.
Progesterone is released from the part of the ovary from which the egg came called the corpus luteum and makes the uterus more fertile to implantation of an embryo, which is necessary for pregnancy.
How does Amenorrhoea occur?
Amenorrhoea may occur as a result of dysfunction at any phase of the circle.
The hypothalamus,
The pituitary gland,
The ovary,
may be responsible for the amenorrhoea.
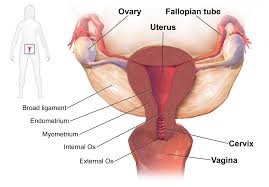
On the other hand, abnormalities in the uterus, vagina, and cervix may also be responsible for amenorrhoea.
Causes of Amenorrhoea
Hypothalamus:
Primary amenorrhoea means failure of a period to start by the age of 16, in the presence of otherwise normal growth and development of secondary sexual characteristics (breast development, pubic hair).
Secondary amenorrhoea means cessation of periods for six months or more after normal puberty and menstruation have occurred.
What is menstruation?
Menstruation is the cyclical loss of the endometrium layer of the uterus, which occurs as a result of a complex interaction between hormones in the brain and the ovaries.
The normal menstrual cycle is about 28 days and starts on the first day of menses.
the whole, menstrual periods are divided 3 phase these are..
1 Follicular phase.
2 ovulatory phase.
3 Luteal phase.
1 Follicular phase.
The follicular phase starts on the first day of menses and ends with ovulation. During the first 14 days of this cycle known as the follicular phase.In this phase
the hypothalamus releases a hormone called gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which stimulates the release of two hormones (follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)) from the pituitary gland.
2 ovulatory.
In the middle of this cycle, the ovary is stimulated to release an egg in a process called ovulation.
Duration of the ovulatory phase is the end of the follicular phase and the beginning of the luteal phase.
3 luteal phase.
Progesterone is released from the part of the ovary from which the egg came called the corpus luteum and makes the uterus more fertile to implantation of an embryo, which is necessary for pregnancy.
How does Amenorrhoea occur?
Amenorrhoea may occur as a result of dysfunction at any phase of the circle.
The hypothalamus,
The pituitary gland,
The ovary,
may be responsible for the amenorrhoea.
On the other hand, abnormalities in the uterus, vagina, and cervix may also be responsible for amenorrhoea.
Causes of Amenorrhoea
Hypothalamus:
- Eating disorders.
- Excessive exercise.
- Mental stress.
- A brain tumor
- Brain surgery or injury
- Hemochromatosis
- genetic abnormality.
- premature ovarian failure,
- polycystic ovarian syndrome(PCOS)
- pregnancy
- uterus abnormality
- Imperforate hymen.
- Transverse vaginal septum.
- Vaginal abnormality.
Treatment:
Treatment depends on their causative agent.
Treatment depends on their causative agent.
Need some test for confirmation of the cause of amenorrhoea.
Oral contraceptive is useful for restart circle
Medications to help relieve the symptoms of PCOS
Clomiphene citrate is helpfull for trigger ovulations
Estrogen replacement therapy (ERT)
Health outcome:
Regular follow up by a specialist physician.
Ensuring adequate nutrition,
Including vitamin D
And calcium intake
Exercise
Ensuring adequate nutrition,
Including vitamin D
And calcium intake
Exercise











No comments